![[Podcast] Green Finance and Sustainable Development in the Southeast – Part 1: Experiences from some Countries](/images/upload/img_background/ueh-bg-101423-082923.jpg)
[Podcast] Green Finance and Sustainable Development in the Southeast – Part 1: Experiences from some Countries
The Southeast of Viet Nam is an important economic driving force of the country; on the other hand, the negative externalities from production and consumption activities of the region are seriously affecting the environment. Facing this problem, the authors of University of Economics Ho Chi Minh City (UEH) has conducted a study on green finance in accordance with the theoretical foundation through analyzing the current situation and lessons learned from some countries, from which, proposing relevant recommendations to promote the application of green finance policies effectively and synchronously in the Southeast region towards one sustainable development and adaptation to regional climate change.

Source: Collected photo
In this first part of the article, the authors introduced the concepts of “Green finance” and solutions for green finance in some countries.
What is Green Finance?
In recent years, green financial solutions have gradually received more attention, research and discussion. The research review indicates that many different definitions of “Green Finance” are available. According to Chowdhury et al. (2013), green finance refers to financial policies aimed at creating incentives to encourage businesses and consumers towards changing their production and consumption behaviors in a more environmental-friendly manner. More specifically, according to the European Investment Bank (2017), green finance is defined as financial services provided for economic activities to support environmental improvement and climate change mitigation and resource use more efficiently. These activities include funding, operation management and risk management of projects aimed at environmental protection, energy saving, clean energy, green transport and green building. In a general way, Green finance can be understood, according to the definition of the UNEP Program, as follows: Green finance implies the solutions towards sustainable development and climate change adaptation through products and financial services provided by financial institutions. In other words, green finance is understood to increase the level of financial flows (from banking, microcredit, insurance and investment) from diverse sources (public sector, private sector and non- profit governmental organizations) for sustainability and climate change adaptation priorities. Since then, negative environmental and social externalities are effectively resolved. Funded projects are not only geared towards profit but also create environmental benefits; concurrently, greater accountability is required.
According to UNEP, Green finance solutions, compared to previous approaches, are multi-dimensional coordination between government, businesses and people as illustrated in Figure 1. In particular, the Government plays an important role in the application, the regulation and the orientation of green finance solutions in multi-ways. At the national level, public finance solutions can be promoted through changes in national regulatory frameworks, harmonization of public finance solutions and strengthening of green financial solutions from different fields. Meanwhile, the local governments play an important role in regulating the financial decision-making process of businesses, promoting the private sector to pay more attention to environmental aspects in line with the sustainable development goals of the region, increasing investment in clean sectors and green technology as well as financing a green economy based on sustainable natural resources.

Figure 1: Multi-dimensional partnership to promote the development of Green finance. Source: UNEP
Green finance solutions in some countries
* China
According to the European Investment Bank (2017), China is at an important stage of economic structural adjustment and development model transformation. Accordingly, the need for green finance to support green industries and sustainable development is constantly increasing. In general, the main green finance solutions that the country is implementing can be summarized into the following main contents as follows:
• Strongly developing green credit.
• Enhancing the role of the stock market in supporting green investment.
• Forming a Green Development Fund and mobilizing social capital through Public & Private Partnerships (PPP).
• Green Insurance Development.
• Improving the emission rights trading market and develop related financial instruments.
• Supporting local government initiatives to develop green finance.
• Promoting International Cooperation on Green Finance.
• Hedging financial risks and strengthening implementation
* Korea
The Korean government implements Green Finance solutions by 2018 through the Climate Change Preparedness Plan. In general, green financial solutions in Korea are promoted and developed synchronously in accordance with the following main policies:
(1) Formation of funding funds for environmental protection activities
The Korean government creates state environmental funds listed as the Green Climate Fund or the Environmental Protection Fund. Through these funds, the Korean Ministry of Environment grants credits for environmentally friendly industrial production listed as the development of new energy or the use of renewable energy.
(2) Promoting the participation of financial institutions in green financial solutions
The Korean government, besides environmental funding funds, encourages domestic and foreign commercial banks to participate in green financial solutions such as green credit support policies. Commercial banks as well as other financial institutions are involved in these solutions. For example, in 2017, the National Pension Service (NPS) invested 200 billion won in two private greeen funds (Green Private Equity Funds - PEFs) to build green domestic infrastructures listed as renewable energy power plants, waste treatment plants and so on.
(3) Developing green bond market
Unlike some countries, green bonds in Korea are usually not government bonds. A common type of green bond is a corporate bond, issued to the public to finance environmental or renewable energy projects. For example, in 2016, Hyundai finance company issued green bonds to finance the purchase of hybrid vehicles.
(4) Creation of an emission right trading market
The Korean government officially launched the Emission Trading Scheme (ETS) market in 2015 with the aim of effectively reducing emissions in different sectors of the economy.
* Singapore
From the point of view of the Singapore government, effective green finance solutions are a combination that considers all three key involved areas: Environment, Society, and Governance (ESG). Investors and companies are paying more and more attention to ESG performance and realizing that it can have a definite impact on a company’s reputation, value, business and investments. Accordingly, Singapore, to promote this mechanism in business, focuses on the deeper integration of ESG issues into financial institutions in Singapore in order to maximize its positive impact on the environment. In the recent years, the Singapore government is promoting ESG integration within the financial sector. More research and development activities in ESG products, expanding the available green financial products and promoting the green bond market. The Singapore Stock Exchange (SGX) has made strict ESG compliance mandatory for all listed companies starting from 2018.
ESG can be understood as linking corporate sustainability standards with investment decisions. In various sectors, ESG criteria have emerged as one way to help investors understand and assess the resilience and long-term sustainability of investments. In general, the application of the Principles for Responsible Investment (PRI) of the United Nations to incorporate ESG issues in Singapore's green finance policy can be generalized as follows:
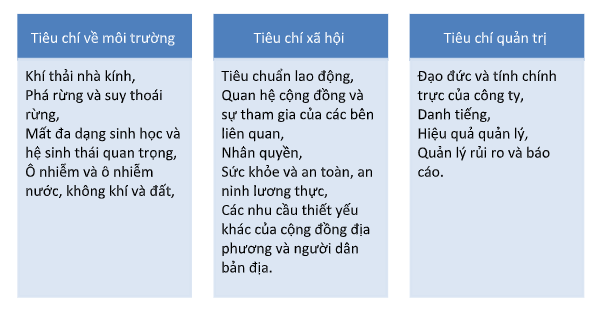
Table 1: Application of ESG criteria in Singapore’s green finance
Accordingly, the sectors rated as high risk are agriculture, chemicals, defense, fossil fuel energy, forestry, infrastructure, mining and metals, and waste management. These industries are given special consideration upon adopting responsible financial policies regarding their business model and level of risk.
In short, Green financial solutions are understood as a combination of many solutions. In order to absolutely effectively solve environmental problems, green finance solutions need to be developed synchronously. In particular, the application of ESG criteria can be a possible solution to improve the environmental efficiency of green finance and to create a foundation for the sustainable development of the Southeast region.
Author: Dr. Trần Trung Kiên, Faculty of Public Finance – University of Economics Ho Chi Minh City (UEH)
This is an article in the series of articles spreading research and applied knowledge from UEH with the “Research Contribution For All - Nghiên Cứu Vì Cộng Đồng” message, UEH cordially invites readers to watch the next Newsletter ECONOMIC No #82.
News, photos: Author, UEH Department of Marketing and Communication
Voice of: Ngoc Quy


![[Podcast] Does the Financial Flexibility Prevent Stock Price Crash Risk during COVID-19 Crisis? Evidence from the Vietnamese Stock Market](https://en.ueh.edu.vn/images/upload/thumbnail/ueh-thumbnail-114718-071624.png)
![[Podcast] An Evaluation Of Two Business English Course Books, Business Partner B1+ Business Partner B2: Students’ And Teachers’ Perspectives](https://en.ueh.edu.vn/images/upload/thumbnail/ueh-thumbnail-113649-071624.png)


![[Podcast] Latest approaches for sustainable universities](https://en.ueh.edu.vn/images/upload/thumbnail/ueh-thumbnail-042022-071224.png)